Interest rates are like the secret sauce in the world of finance—everyone talks about them, but not everyone understands how they work. Whether you're saving for your dream vacation, trying to pay off student loans, or investing in stocks, interest rates play a crucial role in shaping your financial decisions. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about interest rates in a way that’s easy to digest and super actionable.
Let’s face it—finance can feel overwhelming at times. You hear terms like "prime rate," "APR," and "Federal Reserve" thrown around in the news, and suddenly your head starts spinning. But don’t worry! We’ve got your back. By the end of this guide, you’ll not only understand what interest rates are but also how they impact your daily life.
Interest rates aren’t just for economists or bankers—they affect everyone, from the average Joe trying to buy a house to entrepreneurs looking to expand their businesses. So, buckle up because we’re about to dive deep into the world of interest rates, and by the end of this journey, you’ll be able to make smarter financial decisions.
Read also:Santa Clara Makes 16 3pointers In 10162 Win Over Uc Riverside In Nit
Table of Contents
- What Are Interest Rates?
- Types of Interest Rates
- Factors Affecting Interest Rates
- How Interest Rates Impact You
- The Role of the Federal Reserve
- Historical Trends of Interest Rates
- Calculating Interest Rates
- Common Misconceptions About Interest Rates
- Tips for Managing Interest Rates
- Conclusion
What Are Interest Rates?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Simply put, interest rates are the cost of borrowing money. When you take out a loan or use a credit card, the lender charges you a percentage of the amount you borrow as interest. It’s like a fee for using someone else’s cash. But here’s the thing—interest rates aren’t just one number. They come in all shapes and sizes, depending on the type of loan, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the overall economic climate.
For example, if you’re shopping around for a mortgage, you’ll notice that different banks offer different rates. Some might give you a fixed rate, which stays the same throughout the life of the loan, while others might offer an adjustable rate, which can fluctuate based on market conditions. Confusing, right? Don’t worry—we’ll break it down further in the next section.
Why Are Interest Rates Important?
Interest rates are more than just numbers on a piece of paper. They influence everything from the cost of your monthly mortgage payments to the return you earn on your savings account. When rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can stimulate economic growth. On the flip side, when rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down spending and inflation.
Think of interest rates as the thermostat of the economy. Just like how you adjust the temperature in your home to keep it comfortable, central banks adjust interest rates to keep the economy running smoothly. If inflation gets too high, they might raise rates to cool things down. If the economy is sluggish, they might lower rates to give it a boost.
Types of Interest Rates
Not all interest rates are created equal. There are several types of interest rates, each with its own purpose and impact. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ones:
- Prime Rate: This is the rate that banks charge their most creditworthy customers. It’s often used as a benchmark for other interest rates, like mortgage rates and credit card rates.
- Federal Funds Rate: This is the rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight. It’s set by the Federal Reserve and has a huge impact on the overall economy.
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): This is the total cost of borrowing, including interest and fees, expressed as an annual rate. It’s commonly used for credit cards and loans.
- Fixed vs. Variable Rates: Fixed rates stay the same throughout the life of the loan, while variable rates can change based on market conditions.
Understanding these different types of rates can help you make better financial decisions. For instance, if you’re shopping for a car loan, you’ll want to compare the APRs offered by different lenders to get the best deal.
Read also:Final Injury Status For Cleveland Cavaliers Allstar Vs Clippers
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
So, what makes interest rates go up or down? There are several factors at play:
- Inflation: When inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases, so lenders charge higher interest rates to compensate for the loss of value.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can lead to higher interest rates as lenders anticipate increased demand for loans.
- Central Bank Policies: The Federal Reserve and other central banks play a big role in setting interest rates. They use monetary policy tools to influence rates and stabilize the economy.
- Creditworthiness: Your credit score and financial history can affect the interest rates you’re offered. Borrowers with higher credit scores typically get lower rates.
It’s a complex web of factors, but understanding them can help you predict how interest rates might change in the future and plan accordingly.
How Central Banks Control Rates
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the U.S., have a lot of power when it comes to interest rates. They use tools like open market operations and reserve requirements to influence rates. For example, if the Fed wants to lower rates, it might buy government bonds, which increases the money supply and drives rates down. Conversely, if it wants to raise rates, it might sell bonds, which decreases the money supply and drives rates up.
It’s like a game of chess, where every move has consequences. Central banks have to carefully balance their actions to avoid causing economic instability.
How Interest Rates Impact You
Interest rates don’t just affect big corporations and financial institutions—they have a direct impact on your everyday life. Here are a few ways:
- Mortgages: If you’re buying a house, interest rates will determine how much you pay each month. A small change in rates can make a big difference over the life of the loan.
- Credit Cards: High interest rates on credit cards can make it difficult to pay off balances, leading to a cycle of debt.
- Savings Accounts: When rates are low, you earn less on your savings. But when rates are high, your money grows faster.
- Investments: Interest rates can affect the stock market and bond yields, impacting your investment portfolio.
Knowing how interest rates affect you can help you make smarter financial decisions. For example, if you see rates starting to rise, you might want to lock in a fixed rate on your mortgage before they go any higher.
The Role of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. One of its main responsibilities is to manage monetary policy, which includes setting interest rates. The Fed uses interest rates as a tool to control inflation and promote economic growth.
When the economy is overheating and inflation is rising, the Fed might raise interest rates to cool things down. Conversely, during a recession, the Fed might lower rates to stimulate borrowing and spending. It’s a delicate balancing act, and the Fed has to be careful not to overdo it in either direction.
How the Fed Sets Rates
The Fed sets interest rates through its Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which meets several times a year to discuss monetary policy. During these meetings, the committee reviews economic data and decides whether to raise, lower, or keep rates the same.
The FOMC’s decisions have far-reaching effects. For example, if the Fed raises rates, it can lead to higher mortgage rates, car loan rates, and credit card rates. Businesses might also delay investments, which can slow down economic growth.
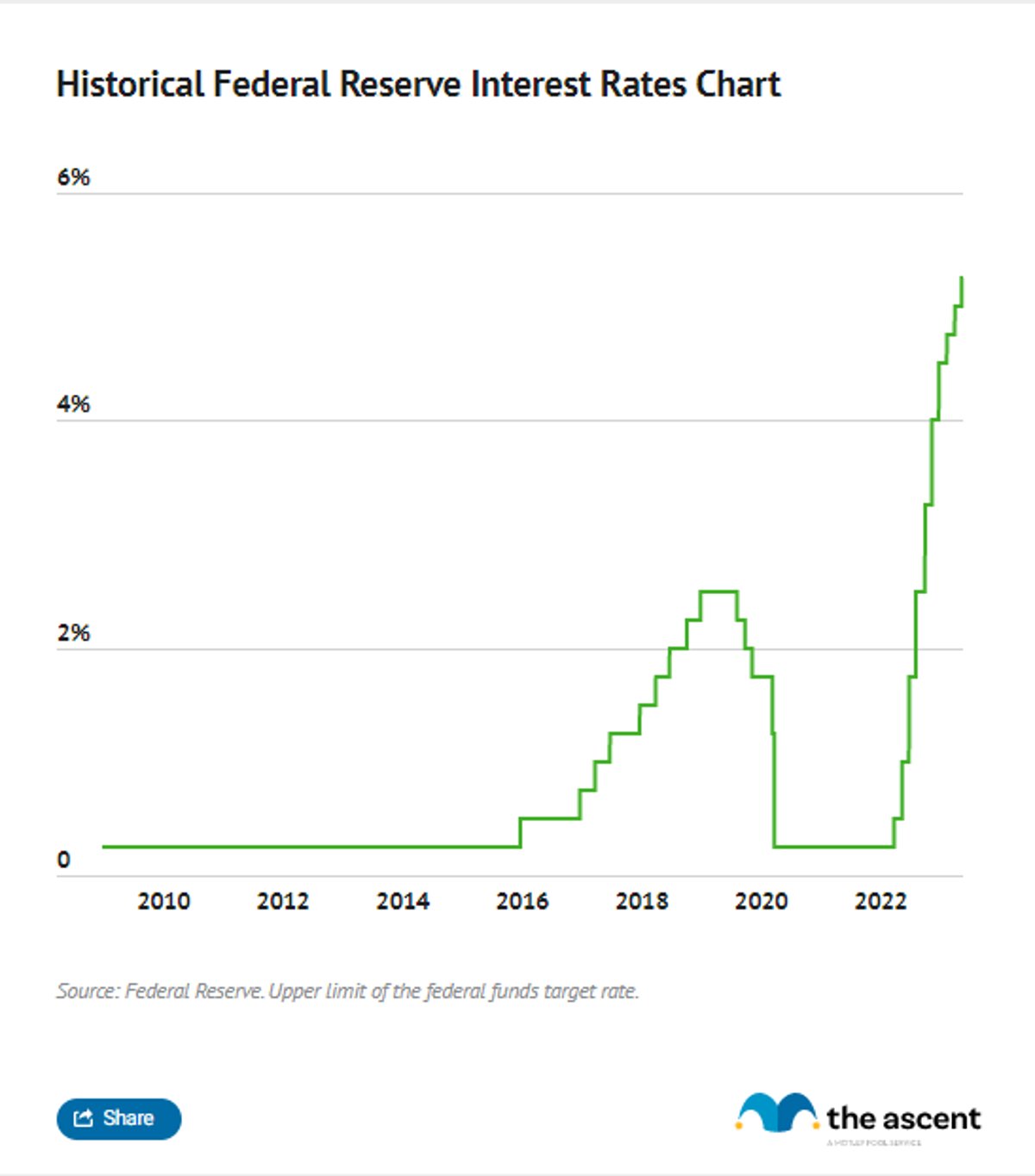
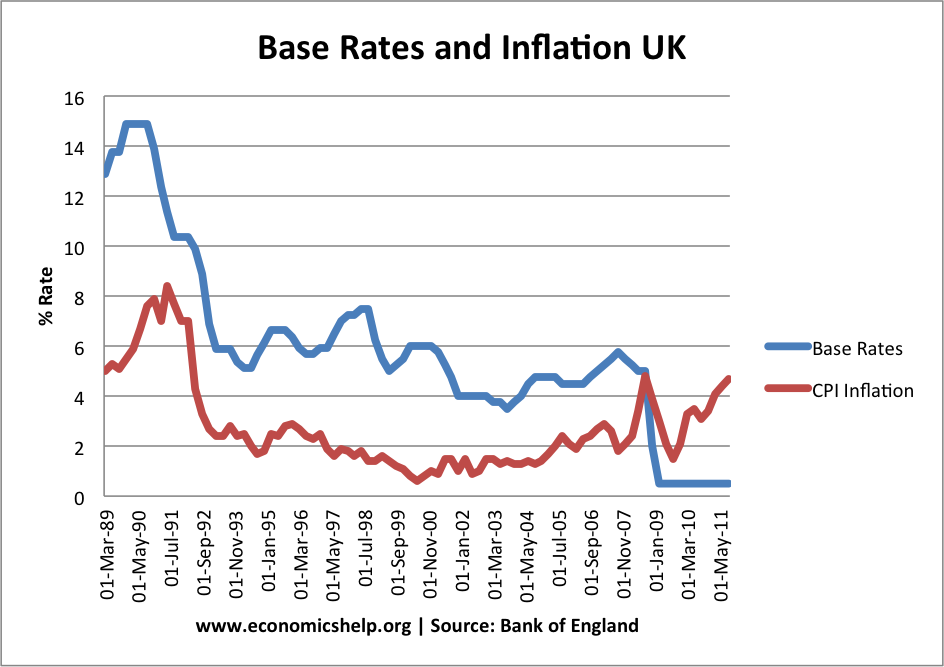
Historical Trends of Interest Rates
Interest rates haven’t always been where they are today. Over the years, they’ve gone through ups and downs, reflecting changes in the economy and global events. Let’s take a look at some historical trends:
- 1980s: Interest rates were sky-high in the 1980s, with the prime rate reaching over 20% at one point. This was largely due to high inflation, which the Fed was trying to tame.
- 2000s: Rates dropped significantly in the early 2000s, leading to a housing boom. But when the housing bubble burst in 2008, the Fed lowered rates to near-zero to stimulate the economy.
- 2020s: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed kept rates near-zero to support economic recovery. As the economy rebounded, rates began to rise again.
History has shown that interest rates are constantly evolving, and understanding these trends can help you prepare for the future.
Calculating Interest Rates
Calculating interest rates might sound complicated, but it’s actually pretty straightforward. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Simple Interest: This is the most basic type of interest calculation. It’s calculated by multiplying the principal amount by the interest rate and the time period.
- Compound Interest: This is where things get interesting (pun intended). Compound interest is calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest of previous periods.
For example, if you have a savings account with a 5% annual interest rate and you start with $1,000, after one year you’ll have $1,050. But if the interest is compounded monthly, you’ll end up with slightly more because the interest is added to the principal each month.
Using Interest Rate Calculators
Thankfully, you don’t have to do all the math yourself. There are plenty of online interest rate calculators that can do the work for you. Just enter the principal amount, interest rate, and time period, and the calculator will give you the total interest and final amount.
These calculators are a great tool for planning your finances, whether you’re saving for a house, paying off debt, or investing in the stock market.
Common Misconceptions About Interest Rates
There are a lot of myths and misconceptions about interest rates floating around. Let’s bust some of them:
- Myth: Lower Rates Always Mean Cheaper Loans: While lower rates generally mean cheaper borrowing, other factors like fees and terms can still make a loan expensive.
- Myth: Interest Rates Only Affect Borrowers: Actually, interest rates affect everyone, including savers and investors. Higher rates can mean higher returns on savings, but they can also lead to lower stock prices.
- Myth: The Fed Controls All Interest Rates: While the Fed has a lot of influence, it doesn’t control every rate. For example, mortgage rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including market demand and housing supply.
Understanding these misconceptions can help you make more informed financial decisions.
Tips for Managing Interest Rates
Now that you know the ins and outs of interest rates, here are some tips for managing them:
- Monitor Economic Indicators: Keep an eye on inflation, GDP growth, and other economic indicators to get a sense of where rates might be headed.
- Lock in Fixed Rates When Possible: If you’re worried about rates rising, consider
![Buying a Home? Mortgage Rate Guide for Singapore [2023]](https://blog.roshi.sg/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Singapore-Home-Loan-Rates-2022.jpeg)